■ Overview
The event calendar site “Ashita wa Harerukana” is a community–AI co-created regional information platform based in Aizu and Fukushima, Japan.
Working as a support staff member at a welfare facility, R-san collaborated with ChatGPT to build numerous features—event submission forms, automatic facility generation, a regional wiki, an AI-powered link directory, and more—despite having very limited development time.
This is a practical case study of Vibe Coding (AI implementation × human verification).
This article focuses on the core concepts behind Vibe Coding. Details of the technical architecture (AI review pipeline, facility auto-generation, AI link pipeline, etc.) are documented on the technical guide page.
【Official Definition of Vibe Coding】
Vibe Coding is:
“AI handles implementation, while the human detects inconsistencies, makes judgments, and directs corrections.”
This iterative development method combines AI-driven implementation with human verification.
Unlike the original meaning of “vibe coding,” meaning “coding by intuition,”
it is a modern collaborative style that positions AI as a high-speed implementation engine and the human as the decision-maker and quality gatekeeper.
→ See the full guide on ChatGPT × WordPress “Context Design” here.
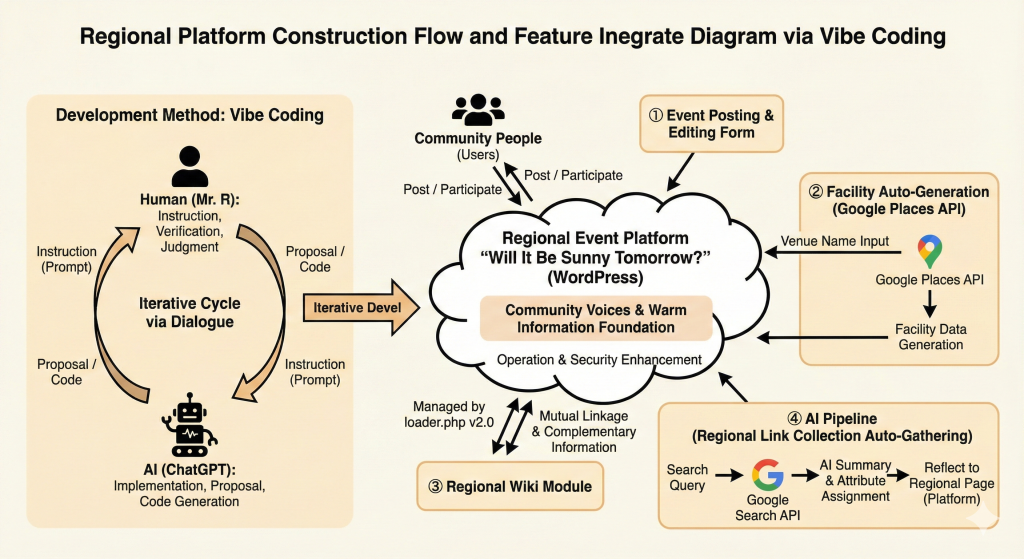
The diagram above illustrates the overall structure and module relationships of the project.
On the left is the iterative “AI implementation × human verification” development loop. The center represents the WordPress-based regional event platform. On the right are major features such as facility auto-generation (Google Places API) and the AI-powered regional link pipeline.
This single visual shows the development process, user flow, AI module roles, and platform integration at a glance.
1. Background and Purpose of Adopting Vibe Coding
Although many small community events take place every day, their information is often scattered and difficult for residents to discover.
Wanting to create a warm, community-driven space where anyone can easily share events, R-san began developing the platform during limited free time.
Because welfare work left little time for development,
the chosen collaborator became ChatGPT.
The human sets the direction, and the AI writes the code.
The human focuses on verification and judgment.
This new development style became the engine behind the entire project.
■ Goals
- A platform created and nurtured by local residents
- A welcoming, participation-friendly posting environment
- A warm information base centered on the voices of the community
2. The Vibe Coding Development Approach
The platform is built through an iterative cycle in which:
R-san handles direction, testing, and verification, while ChatGPT handles code generation and proposals.
This human–AI workflow is called Vibe Coding.
■ Role Distribution
● AI (ChatGPT)
- Generates PHP, JavaScript, and WordPress hook code
- Breaks down and structures specifications
- Identifies likely causes of errors and proposes fixes
- Suggests module designs and improvements
● Human (R-san)
- Tests behavior in the real environment
- Detects inconsistencies or bugs
- Gives specific correction instructions
- Makes final decisions with local and user perspectives
■ Characteristics of This Approach
- The human does not write code—only directs and verifies
- Any inconsistency is corrected immediately
- High-level features can be built through dialogue alone
- Development continues even with very limited time
- Complex systems become achievable for non-engineers
3. Key Features Built Through Vibe Coding
● 1. Event Submission & Editing Form
- User-friendly UI suitable for beginners
- Access-key + session-based authentication
- Automatic email notifications for submitters and admins
- Auto-generated edit links
● 2. Facility Auto-Generation (Google Places API)
- Retrieves address, map URL, and official site from venue names
- Normalizes phone numbers to Japanese format
- Automatically creates facility pages and links them to events
● 3. Regional Wiki Module
- Functions as a local knowledge dictionary
- Edit authentication with access key × session
- Tools for repairing images and removing unused ones
- Improved integration with facility pages
● 4. AI Pipeline (Automated Regional Link Collection)
- Step 0: Generates category-specific search queries
- Step 1: Collects URLs via the Google Search API
- Step 2: Normalization, deduplication, border-region correction
- Step 3: AI summary generation and metadata tagging
- Step 4: Automatic reflection on regional pages
→ Evolved into a data pipeline capable of supporting municipalities nationwide.
● 5. Operational Stability & Safety Enhancements
- Terms of Use v1.2: violation handling and service disclaimer
- loader.php v2.0: unified and optimized module loading order
- Stabilized operations through clarified dependencies
4. Troubles and FAQs from Real Vibe Coding Practice
Here are the main challenges encountered during development, summarized as FAQs.
Q1. Can AI misunderstand the context and generate unintended code?
A: Yes. When multiple specifications are given at once, AI may overwrite existing functionality.
- Parts of the submission form changing unexpectedly
- Deletion of existing features
- Unexpected behavior outside version control
Solution: Provide specifications in smaller, separated chunks and limit the scope of each instruction.
Q2. Can omitted code (“…”) cause critical errors?
A: Yes. If shortened code is pasted as-is, WordPress may display a blank screen.
Solution: A rule was introduced—requested by R-san—to always notify when content is omitted.
Q3. Can removing “unused” files break the system?
A: Yes. WordPress heavily depends on load order and hidden dependencies.
Solution: This issue led to the creation of loader.php v2.0, which resolved such dependency problems.
Q4. Can server environments cause AI-generated code to malfunction?
A: Yes. ConoHa WING × LiteSpeed × PHP-FPM behaves differently from common assumptions in AI output.
- Session inconsistencies
- Incorrect file path assumptions
- Behavior differences due to PHP configuration
Solution: Adjust code iteratively based on live testing in the actual environment.
5. Value Created Through Vibe Coding
● 1. Non-Engineers Breaking Through Technical Barriers
Even without being an engineer, the human can focus on judgment and verification while AI handles implementation—resulting in a professional-grade system.
● 2. High-Speed, Dialogue-Based Development
The “build → test → fix” cycle advances quickly even without formal design documents.
● 3. Building a Foundation for Community Co-Creation
By lowering technical barriers through AI collaboration, the platform enables residents to share information more freely.
6. Future Outlook
- Nationwide expansion of facility data
- Enhanced regional wiki with auto cross-referencing
- Improved posting UI and stronger user participation
- New value creation across “Welfare × AI” and “Community × AI”
The project is supported by a technical foundation combining WordPress, AI, and custom modules. Details on AI review systems, link pipelines, facility auto-generation, and other internal architecture can be found on the AI × WordPress Technical Documentation.
API cost optimization and server operation strategies are summarized in the Cost & Operations Tips section.
開発者プロフィール
Rさん(福祉施設 支援員/地域情報サイト運営/元エンジニア)
福祉現場に従事しながら、余暇時間を使ってChatGPTとの共同開発を推進。
「人は検証と指示、AIはコーディング」という役割分担を確立し、短期間で多機能な地域プラットフォームを構築。
本ページの内容は、2025年9月〜にかけてRさんとChatGPTが実際に構築した
「明日は晴れるかな」プロジェクトの開発記録に基づいています。
制作:ChatGPT(AI生成)
監修:Rさん(R2Fish Project)
本ページは ChatGPT が生成した初稿をもとに、
Rさんが技術精度・構成を監修し “実務で使える形” に仕上げた共同制作コンテンツです。